4.9 KiB
| title | author | theme | mainfont | fontsize |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpenLDAP | Akshay Pushparaj | Berlin | Iosevka | 8pt |
Introduction to LDAP
What is LDAP?
LDAP or Lightweight Directory Access Protocol is a standards-based protocol for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services. LDAP has always been considered a standard for user management in organizations of all sizes.
What is directory service?
- Directory is a specialized database specifically designed for searching and browsing, in additional to supporting basic lookup and update functions.
- Directories tend to contain descriptive, attribute-based information and support filtering capabilities.
- Directories generally do not support complicated transaction or roll-back schemes found in database management systems designed for handling high-volume complex updates.
- Directories are generally tuned to give quick response to high-volume lookup or search operations.
What kind of information can be stored in the directory?
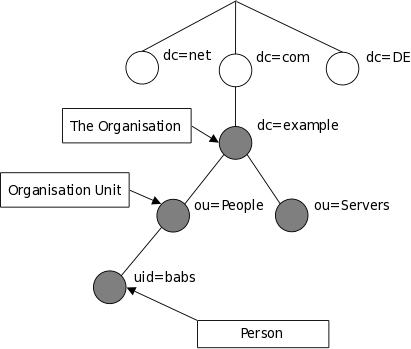
LDAP information model is based on entries. An entry is a collection of attributes that has a globally-unique Distinguished Name (DN). The DN is used to refer to the entry unambiguously. Each of the entry's attributes has a type and one or more values.
How is the information arranged?
Directory entries are arranged in a hierarchical tree-like structure.
 {#id .class width=200 height=200 display=block}
{#id .class width=200 height=200 display=block}
Differences between traditional databases
- LDAP is a open standard protocol.
- LDAP is heavily read optimized.
- LDAP is lightweight.
Usecases
Some of the usecases of LDAP are:
- Machine Authentication
- User Authentication
- User/System Groups
- Address book
- Organization Representation
- Asset Tracking
- Telephony Information Store
- User resource management
- E-mail address lookups
- Application Configuration store Machine Authentication
- etc
OpenLDAP
What is OpenLDAP?
- OpenLDAP is an free and open source implementation of LDAP. The project started at University of Michigan, now maintained by the OpenLDAP Foundation.
Features
- Lightweight
- Supports a wide variety of backends or databases.
- Supports components called overlays which can be used to customize backend behaviour without the need to write a custom backend.
- Has support for wide variety of OS and services.
- OpenLDAP is highly flexible. Has code-reliant functionality which doesn’t lock users into predetermined workflows; rather, we can manipulate the software to our exact needs.
Cons
- Directory configuration and management are manual. Hence it is more time consuming and has a higher learning curve.
- OpenLDAP is a command-line application. However there are multiple LDAP browsers available which can be used in case a UI is required. Few of them listed below:
Other free software LDAP implementations
389 DS
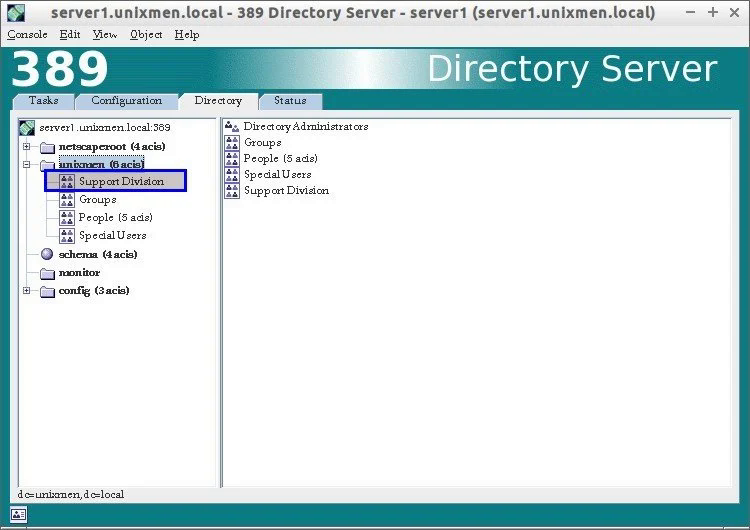
- Like OpenLDAP, 389 DS or 389 Directory Server is a LDAP implementation by RedHat as part of the community-supported Fedora project.
- 389 DS have a graphical interface that can be used for administration.
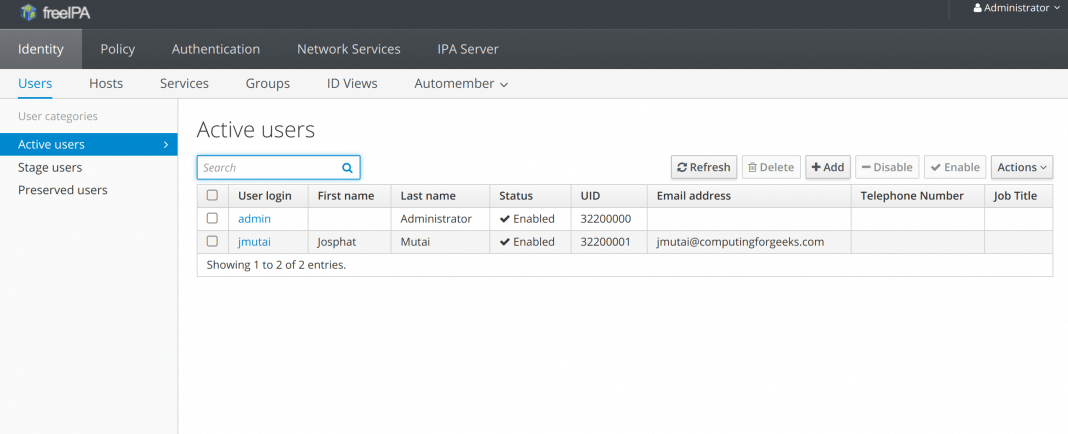
FreeIPA
-
FreeIPA is an identity management system created by RedHat. The aim with FreeIPA is to provide a centrally managed Identity, Policy and Audit(IPA) system.
- Identity management ensure the right users have appropriate access to resources.
- Security policies are a set of requirements to maintain a safe and secure computing environment.
- Audit trail are records of events, procedures or operations being done on the system.
-
FreeIPA uses a combination of different software inorder to acheive an IPA system. It uses Fedora, 389 DS, Kerberos, DNS, SSSD and other free and open source components.
-
The advantage of using FreeIPA is that it is easy to setup. Since everything is taken care by FreeIPA for us it has less flexibilty comapred to OpenLDAP.
-
FreeIPA has a Web UI for administration.
Samba
- Samba runs on Unix platforms, but speaks to Windows clients like a native. It allows a Unix system to move into a Windows "Network Neighborhood" without causing a stir. Windows users can happily access file and print services without knowing or caring that those services are being offered by a Unix host.
- Samba is an open source CIFS implementation. CIFS or Common Internet File System is a protocol suite used to share files remotely via IP.
- Samba allows for a Linux server to act as a Domain Controller. By doing so, user credentials on the Windows domain can be used instead of needing to be recreated and then manually kept in sync on the Linux server.
- A domain controller is a server that manages network and identity security, effectively acting as the gatekeeper for user authentication and authorization to IT resources within the domain.