|
|
7 years ago | |
|---|---|---|
| util | 7 years ago | |
| .gitignore | 7 years ago | |
| 92263853ad.config | 7 years ago | |
| LICENSE | 7 years ago | |
| LICENSE.microcode | 7 years ago | |
| NEWS | 7 years ago | |
| README.md | 7 years ago | |
| flashrom_rpi_bottom_unlock.sh | 7 years ago | |
| flashrom_rpi_top_write.sh | 7 years ago | |
| front.jpg | 7 years ago | |
| pci8086,0166.rom | 7 years ago | |
| prepare_internal_flashing.sh | 7 years ago | |
| release.sh | 7 years ago | |
| rpi_clip.jpg | 7 years ago | |
README.md
coreboot-x230
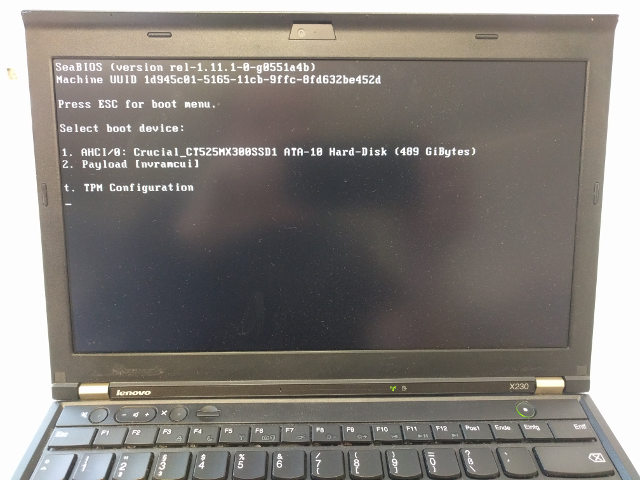
pre-built coreboot image and documentation on how to flash them for the Thinkpad X230. SeaBIOS is used, to be compatible with Windows and Linux, and to be easy to use: simply a boot menu and a few options to tick.
We want to make it easy to "bootstrap" an X230 to a working, unlocked, up-to-date coreboot-based BIOS.
Latest release (config overview and version info)
- coreboot-x230 0.0.5 - see our release page
- The only proprietary binary, the VGA BIOS is executed in "secure" mode (PCI_OPTION_ROM_RUN_YABEL)
coreboot
- We simply take coreboot's current state in it's master branch at the time we build a release image. That's the preferred way to use coreboot. The git revision we use is always included in the release.
Intel microcode
- revision
1ffrom 2018-02-07 (Intel package 20180312 not yet in coreboot upstream) under Intel's license
SeaBIOS
- version 1.11.1 from 2018-03-19 (part of coreboot upstream)
table of contents
- TL;DR
- Flashing for the first time
- How to update
- When do we do a release?
- How we build
- Why does this work
- Alternatives
TL;DR
For first-time flashing, remove the keyboard and palmrest, and (using a
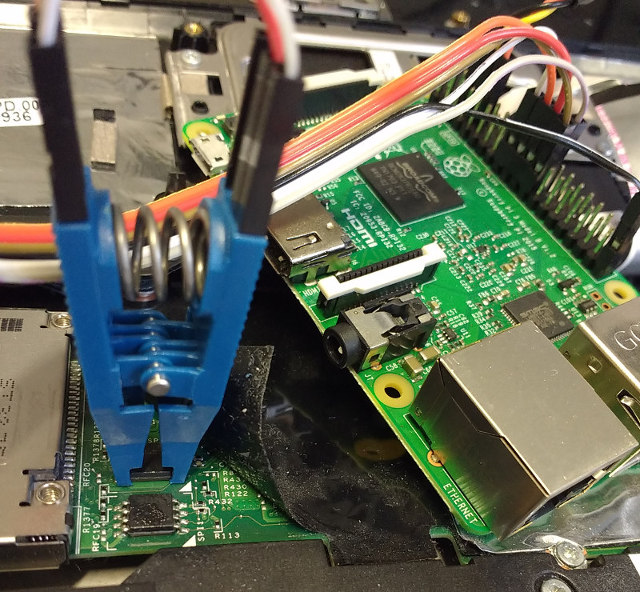
Raspberry Pi with a SPI 8-pin chip clip connected), run
flashrom_rpi_bottom_unlock.sh on the lower chip
and flashrom_rpi_top_write.sh on the top chip of the two.
For updating later, run prepare_internal_flashing.sh to get
files and instructions about updating. No need to disassemble.
Flashing for the first time
Especially for the first time, you must flash externally. See below for the details for using a Rapberry Pi, for example.
flashrom chip config
We (or our scripts) use flashrom for flashing. Run
flashrom -p <your_hardware> (for example
flashrom -p linux_spi:dev=/dev/spidev0.0,spispeed=128 for the
Raspberry Pi) to let flashrom detect the chip.
It will probably list a few you need to choose from when flashing
(by adding -c <chipname>). Please review the chip model for your device.
In case you are unsure what to specify, here's some examples we find out there:
4MB chip
MX25L3206Eseems to mostly be in use
8MB chip
MX25L6406E/MX25L6408Eis used in this guideMX25L3206E/MX25L3208Eis seen working with various X230 models.EN25QH64is used sometimes
EC firmware (optional)
Enter Lenovo's BIOS with F1 and check the embedded controller (EC) version to be 1.14 and upgrade using the latest bootable CD if it isn't. This updates BIOS and EC. The EC cannot be upgraded when coreboot is installed. (In case a newer version should ever be available (I doubt it), you could temporarily flash back the original Lenovo BIOS image from your backup)
ifd unlock and me_cleaner: the 8MB chip
The Intel Management Engine resides on the 8MB chip (at the bottom, closer to you). We don't need to touch it for coreboot-upgrades in the future, but to enable internal flashing, we need to unlock it once. We run ifdtool and, while we are at it, me_cleaner on it:
We support using a RPi, see below for the connection details. Move the release-tarball to the RPi (USB Stick or however) and unpack it (to the current directory and change into it):
mkdir tarball_extracted
tar -xf <tarball>.tar.xz -C tarball_extracted
cd tarball_extracted
And finally unlock the 8M chip by using the included script (be patient):
sudo ./flashrom_rpi_bottom_unlock.sh -m -c <chipname> -k <backup.bin>
That's it. Keep the backup safe.
background (just so you know)
-
The
-moption above also runsme_cleaner -Sbefore flashing back. -
The
-loption will (re-)lock your flash ROM, in case you want to force yourself (and others) to hardware-flashing externally. -
If you don't use a RPi, change the flashrom programmer to your needs.This is roughly what's going on:
flashrom -p linux_spi:dev=/dev/spidev0.0,spispeed=128 -c "MX25L6406E/MX25L6408E" -r ifdmegbe.rom flashrom -p linux_spi:dev=/dev/spidev0.0,spispeed=128 -c "MX25L6406E/MX25L6408E" -r ifdmegbe2.rom diff ifdmegbe.rom ifdmegbe2.rom git clone https://github.com/corna/me_cleaner.git && cd me_cleaner ./me_cleaner.py -S -O ifdmegbe_meclean.rom ifdmegbe.rom ifdtool -u ifdmegbe_meclean.rom flashrom -p linux_spi:dev=/dev/spidev0.0,spispeed=128 -c "MX25L6406E/MX25L6408E" -w ifdmegbe_meclean.rom.new
BIOS: the 4MB chip
(internally, memory of the two chips is mapped together, the 8MB being the lower part, but we can essientially ignore that). Again, using a RPi is supported here. We assume you have the unpacked release tarball ready, see above. Use the following included script:
sudo ./flashrom_rpi_top_write.sh -i x230_coreboot_seabios_<hash>_top.rom -c <chipname> -k <backup>
That's it. Keep the backup safe.
How to update
When upgrading to a new release, only the "upper" 4MB chip has to be written. Download the latest release image we provide and flash it:
Example: internal
CAUTION: THIS IS NOT ENCOURAGED
- Only for updating! You have to have your 8MB chip flashed externally using
our
flashrom_rpi_bottom_unlock.shscript (ifdtool -u) before this, once - very convenient: just install flashrom on the X230 and software-update, but according to the flashrom manpage this is very dangerous!
- Boot Linux with the
iomem=relaxedboot parameter (for example set in /etc/default/grub) - download the latest release tarball (4MB "top" BIOS image is included) and extract it
- run
prepare_internal_flashing.shfor generating all necessary files and printing all instructions - run the flashrom command you got from the script. That's it.
Example: Raspberry Pi 3
Here you'll flash externally, using a "Pomona 5250 8-pin SOIC test clip". You'll find one easily. This is how the X230's SPI connection looks on both chips:
Screen (furthest from you)
__
MOSI 5 --| |-- 4 GND
CLK 6 --| |-- 3 N/C
N/C 7 --| |-- 2 MISO
VCC 8 --|__|-- 1 CS
Edge (closest to you)
and with our release tarball unpacked, the command you need looks like so:
flashrom_rpi_top_write.sh -i x230_coreboot_seabios_<release>_top.rom -c <chipname>
We run Raspbian and have the following setup
-
Serial connection using a "USB to Serial" UART Adapter and picocom or minicom
-
Yes, in this case you need a second PC connected to the RPi over UART
-
in the SD Cards's
/boot/config.txtfileenable_uart=1anddtparam=spi=on -
For flashrom we put
spi_bcm2835andspidevin /etc/modules -
Connect to a wifi or to network over ethernet to
sudo apt-get flashrom -
only flash the top 4M chip
-
connect the Clip to the Raspberry Pi 3 (there are prettier images too:
Edge of pi (furthest from you) (UART) L GND TX RX CS E | | | | F +---------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ T | x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x | | x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x | E +----------------------------------^---^---^---^-------------------------------^--+ D | | | | | G 3.3V MOSIMISO| GND E (VCC) CLK Body of Pi (closest to you)
Now copy our release tarball over to the Rasperry Pi.
One way to copy, is convertig it to ascii using
uuencode (part of Debian's sharutils package) described below. This is a
direct, shady and slow way to transfer a file. Use a USB
Stick or scp instead. :) (but you need even more hardware or a network).
(convert)
host$ uuencode <tarball> <tarball>.ascii > <tarball>.ascii
(transfer)
rpi$ cat > <tarball>.ascii
host$ pv <tarball>.ascii > /dev/ttyUSBX
(wait)
rpi$ (CTRL-D)
(convert back)
rpi$ uudecode -o <tarball> <tarball>.ascii
(verify)
host$ sha1sum <tarball>
rpi$ sha1sum <tarball>
Now unpack it:
mkdir tarball_extracted
tar -xf <tarball> -C tarball_extracted
cd tarball_extracted
Check the SPI connection to the "top" chip to update, and run:
sudo ./flashrom_rpi_top_write.sh -i x230_coreboot_seabios_<hash>_top.rom -c <chipname>
That's it.
background (just so you know)
- Connecting an ethernet cable as a power-source for SPI (instead of the VCC pin) is not necessary (some other flashing how-to guides mention this). Setting a fixed (and low) SPI speed for flashrom offeres the same stability. Our scripts do this for you.
When do we do a release?
Either when
- There is a new SeaBIOS release,
- There is a new Intel microcode release (for our CPU model),
- There is a coreboot issue that affects us, or
- We change the config
How we build
- Everything necessary to build coreboot (while only the top 4MB are usable of course) is included here
- The task of building coreboot is not too difficult
- When doing a release here, we always try to upload to coreboot's board status project
- If we add out-of-tree patches, we always post them for review upstream
Why does this work?
On the X230, there are 2 physical "BIOS" chips. The "upper" 4MB one holds the actual bios we can generate using coreboot, and the "lower" 8MB one holds the rest that you can modify yourself once, if you like, but strictly speaking, you don't need to touch it at all. What's this "rest"? Mainly a tiny binary used by the Ethernet card and the Intel Management Engine.
Alternatives
We aim to be the easiest possible coreboot distribution for the X230 - both to install and to use. And since our images are unlocked to enable easy software updates, it's easy to try alternative systems too:
- Heads - coreboot distribution with pre-built (or reproducibly buildable) flash images for the X230. Heads includes Linux, with tools to create a trusted boot chain using your GPG key and the TPM.
- libreboot - also a coreboot distribution with pre-built image releases. But the X230 is currently not supported (the X200 is) - libreboot images are built from free software only and include the GRUB bootloader.